Global Decentralized Identities
Certain sections of the documentation are currently redacted and will be available soon. This version is intended for private circulation only.
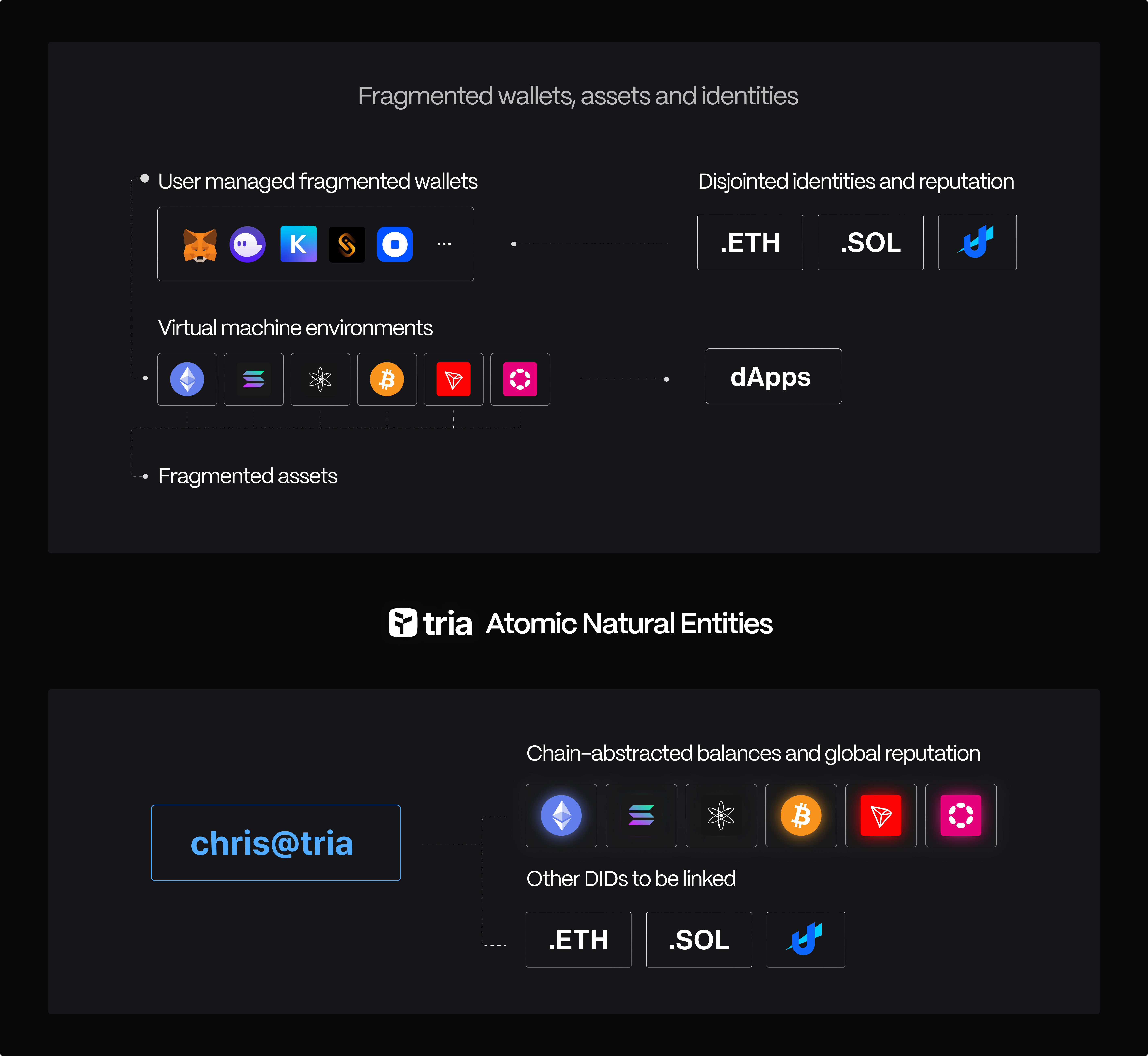
Fragmentation has introduced a host of challenges, impacting not only the fluidity of user journeys and cross-chain asset interoperability but also introducing complexities like aggregating disjointed and inconsistent reputation graphs. Fragmentation stands as a substantial barrier to delivering a cohesive and seamless experience to users interacting with the Web3 ecosystem.
In addition to Single Sign-on (SSO) and external wallets, Tria integrates seamlessly with decentralized identities (DIDs) such as ENS, enabling a global, chain abstracted indentity interface. A @tria decentralized identity (DID) is a blockchain-agnostic identity framework. These unique identifiers combine an independent user-chosen name with a root element, separated by the "@" symbol. Tria prompts users to create (mint) a Tria Decentralized Identifier (DID) upon using our interfaces, effectively serving as their unique, aggregated identity and wallet management stack across Web3.
Atomic Natural Entity - Identities
Traditional interfaces like managing wallets (extensions, mobile apps, web, and hardware wallets) across different ecosystem networks and devices are often complex, and asset fragmentation across wallets, chains, and devices create friction.
Tria's Aggregated Identities addresses the fragmentation of the Web3 wallets, asset management and interoperability centered using the most atomic natural entity – Identities. Identities like a Gmail account is a far more familiar primitive to broader users. By introducing a familiar, identity-first onboarding, powered by Unchained, Tria dismantles traditional chain-specific barriers, crafting a fluent, global and chain-abstracted asset and identity experience.
Functional Specification
Tria presents a novel approach to Decentralized Identity (DID)-first Web3 onboarding and wallet management. Tria's Decentralized Identities function as a mapping service, enabling users to associate a human-readable alias (a @tria name) with their wallet addresses across all blockchains.
@tria DIDs are Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) minted on Unchanined to imbue aliases with additional functionalities and create a marketplace for user-chosen identities. Minting a Tria DID triggers the on-chain minting of a corresponding NFT. This NFT enables users to participate in a decentralized marketplace, engaging in activities like buying, selling, and collecting unique Tria-powered Aggregated DID.
Tria's Aggregated DID consist of two parts – an independent identifier and a root. The independent identifier is the preceding alphanumeric text before '@', and the root is the end of a Tria DID. For instance, in joe@tria - Joe is the name, and tria is the root. Root's are customizable by a root issuer such as a blockchain ecosystem, dApp or enterprise (e.g., vitalik@eth, sandeep@polygon, charlie@litecoin and more).
Tria's DID protocol facilitates automatic address resolution (both forward and reverse) during transactions. When a user interacts with a dApp or on-chain ecosystem, the DID is automatically resolved to the corresponding wallet address (forward resolution). Conversely, upon connecting a wallet address to a dApp, the user's associated the DID is displayed (reverse resolution). This streamlines user experience within dApps and fosters a more intuitive interaction.
Beyond its core functionality, Tria's DID extend support to non-EVM blockchains, effectively operating as a multichain DID service. Users can associate their non-EVM wallet addresses with their Tria DID, enabling forward and reverse resolution within dApps built on these independent blockchains. This promotes interoperability and identity aggregation within the broader multi-chain landscape. Additionally, Tria's DID incorporate support for meta transactions, allowing for seamless integration with relayer services. This facilitates gasless minting of these Identities, further enhancing user experience and promoting wider adoption of the Tria Aggregated DID.
CAIP-275: Domain Wallet Authenticatio
Tria is a part of early Chain Agnostic Improvement Proposals (CAIP-275) adopters alongside Lit Protocol, ENS, and 50+ others. Current blockchain authentication methods primarily rely on connecting wallets via providers like Metamask. However, this requires users to remember both their wallet provider and their wallet address. As more wallets, signers, and chains come online, this problem will only get worse. Crypto domains provide a human-readable, user-friendly way to represent wallet addresses. By enabling authentication directly with crypto domains, this standard aims to improve usability and adoption of web3 logins.
Additionally, standardizing the way domain NFT metadata specifies its supported authentication mechanisms allows any compatible domain NFT to abstract out authentication methods and key management. This abstraction allows both login modals and dApps to easily integrate domain-based logins such as Tria's aggregated DIDs.
Reputation and Credentials
@tria DIDs serve as an enclave for zk credentials, encapsulating complex structures like reputation graphs and reusable zk-KYC. This infrastructure allows users to selectively disclose credentials to dApps on a permissioned basis, enabling high-assurance identity verification without sacrificing data sovereignty. This framework realizes the notion of self-sovereign identity, putting full control over identity data in users hands. Users can reveal only discrete attributes via zk-proofs, preserving privacy by obfuscating the underlying data. this approach permits dApps to validate credentials while maintaining minimal exposure, ensuring the integrity of claims without direct data access.
At Tria, we harbor a conviction that current approaches to wallet management fall short of fully onboarding users to the vast possibilities of Web3. We refuse to accept the status quo of confining users to a single blockchain and compromising the composability of on-chain primitives. Which is why, we are committed to pushing the boundaries of user onboarding and setting a new standard to chain abstracted interfaces.
| Feature | Tria's DID Framework | Status Quo |
|---|---|---|
| Multichain Identities | Yes | No |
| Aggregated reputation | Yes | No |
| Composability with other DID stacks | Yes | No |
| Organisations/Community Roots | Yes | Limited |
| Login with name (CAIP275) | Yes | Partially Supported |
| Credentials/Attestations | Yes | Partially Supported |